GoLang中的iface 和 eface 的区别解析
GoLang之iface 和 eface 的区别是什么?
iface 和 eface 都是 Go 中描述接口的底层结构体,区别在于 iface 描述的接口包含方法,而 eface 则是不包含任何方法的空接口:interface{}。
从源码层面看一下:
type iface struct {
tab *itab
data unsafe.Pointer
}
type itab struct {
inter *interfacetype
_type *_type
link *itab
hash uint32 // copy of _type.hash. Used for type switches.
bad bool // type does not implement interface
inhash bool // has this itab been added to hash?
unused [2]byte
fun [1]uintptr // variable sized
}
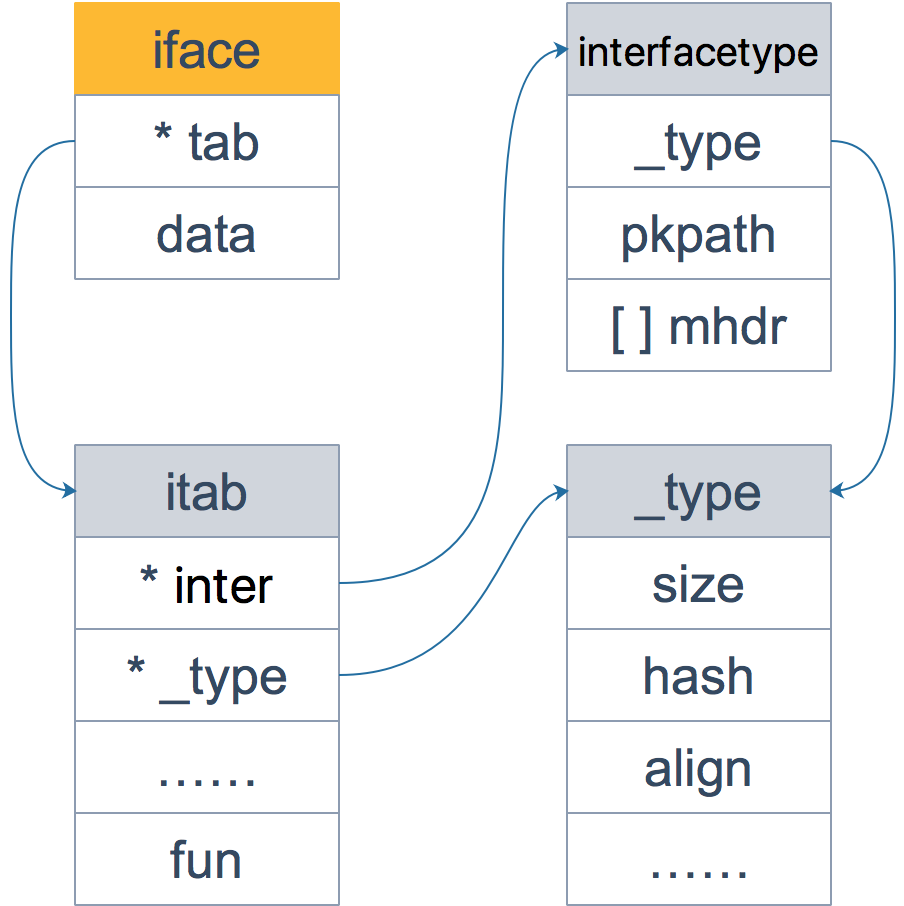
iface 内部维护两个指针,tab 指向一个 itab 实体, 它表示接口的类型以及赋给这个接口的实体类型。data 则指向接口具体的值,一般而言是一个指向堆内存的指针。
再来仔细看一下 itab 结构体:_type 字段描述了实体的类型,包括内存对齐方式,大小等;inter 字段则描述了接口的类型。fun 字段放置和接口方法对应的具体数据类型的方法地址,实现接口调用方法的动态分派,一般在每次给接口赋值发生转换时会更新此表,或者直接拿缓存的 itab。
这里只会列出实体类型和接口相关的方法,实体类型的其他方法并不会出现在这里。如果你学过 C++ 的话,这里可以类比虚函数的概念。
另外,你可能会觉得奇怪,为什么 fun 数组的大小为 1,要是接口定义了多个方法可怎么办?实际上,这里存储的是第一个方法的函数指针,如果有更多的方法,在它之后的内存空间里继续存储。从汇编角度来看,通过增加地址就能获取到这些函数指针,没什么影响。顺便提一句,这些方法是按照函数名称的字典序进行排列的。
再看一下 interfacetype 类型,它描述的是接口的类型:
type interfacetype struct {
typ _type
pkgpath name
mhdr []imethod
}
可以看到,它包装了 _type 类型,_type 实际上是描述 Go 语言中各种数据类型的结构体。我们注意到,这里还包含一个 mhdr 字段,表示接口所定义的函数列表, pkgpath 记录定义了接口的包名。
这里通过一张图来看下 iface 结构体的全貌:
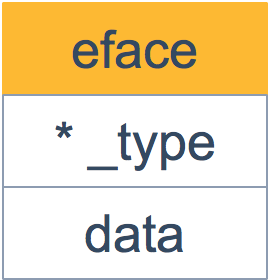
接着来看一下 eface 的源码:
type eface struct {
_type *_type
data unsafe.Pointer
}
相比 iface,eface 就比较简单了。只维护了一个 _type 字段,表示空接口所承载的具体的实体类型。data 描述了具体的值。
我们来看个例子:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
x := 200
var any interface{} = x
fmt.Println(any)
g := Gopher{"Go"}
var c coder = g
fmt.Println(c)
}
type coder interface {
code()
debug()
}
type Gopher struct {
language string
}
func (p Gopher) code() {
fmt.Printf("I am coding %s language\n", p.language)
}
func (p Gopher) debug() {
fmt.Printf("I am debuging %s language\n", p.language)
}
执行命令,打印出汇编语言:
go tool compile -S ./src/main.go
可以看到,main 函数里调用了两个函数:
func convT2E64(t *_type, elem unsafe.Pointer) (e eface) func convT2I(tab *itab, elem unsafe.Pointer) (i iface)
上面两个函数的参数和 iface 及 eface 结构体的字段是可以联系起来的:两个函数都是将参数组装一下,形成最终的接口。
作为补充,我们最后再来看下 _type 结构体:
type _type struct {
// 类型大小
size uintptr
ptrdata uintptr
// 类型的 hash 值
hash uint32
// 类型的 flag,和反射相关
tflag tflag
// 内存对齐相关
align uint8
fieldalign uint8
// 类型的编号,有bool, slice, struct 等等等等
kind uint8
alg *typeAlg
// gc 相关
gcdata *byte
str nameOff
ptrToThis typeOff
}
Go 语言各种数据类型都是在 _type 字段的基础上,增加一些额外的字段来进行管理的:
type arraytype struct {
typ _type
elem *_type
slice *_type
len uintptr
}
type chantype struct {
typ _type
elem *_type
dir uintptr
}
type slicetype struct {
typ _type
elem *_type
}
type structtype struct {
typ _type
pkgPath name
fields []structfield
}
这些数据类型的结构体定义,是反射实现的基础。
关于GoLang之iface和eface的区别是什么的文章就介绍至此,更多相关GoLangiface和eface区别内容请搜索编程宝库以前的文章,希望以后支持编程宝库!
前言go语言并没有面向对象的相关概念,go语言提到的接口和java、c++等语言提到的接口不同,它不会显示的说明实现了接口,没有继承、子类、implements关键词。 一、概述在 Go ...